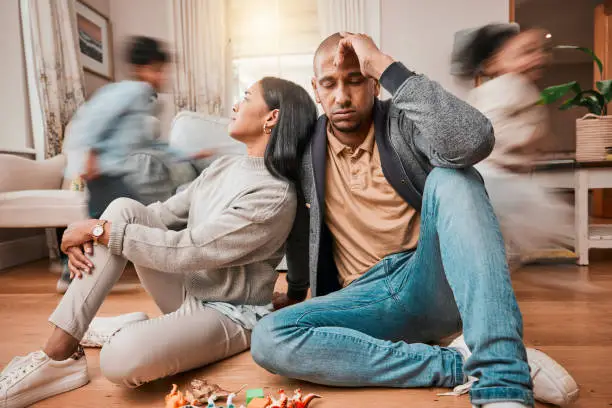
In relationships, whether romantic, familial, or platonic, the terms “possessive behavior” and “healthy attachment” are often used interchangeably. However, they are vastly different in both their emotional impact and the long-term effects they have on individuals and relationships. Understanding the distinction between these two concepts can be crucial for fostering emotionally balanced, healthy connections and avoiding toxic patterns that can lead to resentment, control issues, and emotional strain.
Possessive behavior is often mistaken for deep affection, but it can quickly become unhealthy when it leads to control, jealousy, or manipulation. While healthy attachment fosters security and trust, possessive tendencies can create tension and emotional distress in relationships. In this article, we will explore what is possessive behavior, provide possessive behavior examples, and highlight the key differences between possessive behavior in relationships and a secure emotional bond.
What Is Possessive Behavior?
What is possessive behavior? It stems from deep-seated insecurities and a fear of losing someone. It manifests as an intense need for control over a partner’s actions, friendships, and decisions. Unlike healthy attachment, which is built on mutual trust and respect, possessive behavior often involves:
- Excessive jealousy – Feeling threatened by a partner’s social interactions, even with close friends or family.
- Control over decisions – Dictating what a partner wears, who they spend time with, or where they go.
- Constant need for reassurance – Requiring frequent validation of love and commitment.
- Invasion of privacy – Checking a partner’s phone, emails, or social media without consent.
- Emotional manipulation – Using guilt or threats to control a partner’s behavior.
Recognizing these signs early can prevent unhealthy relationship patterns from escalating. Possessive behavior in relationships can have serious consequences, including emotional abuse, loss of independence, and feelings of entrapment.
Healthy Attachment: A Secure Foundation
Unlike possessive behavior, healthy attachment is rooted in emotional security, open communication, and mutual respect. A securely attached relationship allows both partners to grow individually while maintaining a strong connection. Key characteristics of healthy attachment include:
- Trust and independence – Allowing each other space without constant worry or suspicion.
- Open and honest communication – Expressing concerns without fear of retaliation.
- Emotional support – Encouraging each other’s personal goals and well-being.
- Respect for boundaries – Acknowledging and honoring personal space and privacy.
Healthy attachment fosters love without control, ensuring both partners feel valued and understood. Relationship therapy in New York City can help individuals develop secure attachment styles and strengthen relationship dynamics.
The Key Differences Between Possessive Behavior and Healthy Attachment
At first glance, the difference between possessiveness and healthy attachment might not always seem clear, but there are distinct contrasts that can help you identify which dynamic is at play in a relationship.
1. Control vs. Freedom
- Possessive Behavior: In a possessive relationship, one person tries to control the other’s actions, emotions, and choices. This might include telling them who they can talk to, where they can go, or what they can wear. The goal is often to exert dominance and create a power imbalance, where one person has more influence over the other.
- Healthy Attachment: In a healthy relationship, both individuals feel free to make their own choices without fearing judgment or restriction. While both may choose to prioritize each other, they also support each other’s independence and respect each other’s right to make decisions without interference.
2. Jealousy vs. Trust
- Possessive Behavior: A possessive person often experiences extreme jealousy, which may lead to accusations, spying, or even emotional outbursts. They may feel threatened by other people, even if there’s no valid reason for concern, and this jealousy can erode the trust between both individuals.
- Healthy Attachment: In a healthy relationship, both people trust each other. Jealousy may arise occasionally, but it is handled maturely and doesn’t manifest in controlling or aggressive behavior. Healthy individuals understand that trust is the bedrock of their connection, and they communicate openly when insecurities arise rather than acting on them impulsively.
3. Dependence vs. Independence
- Possessive Behavior: Possessive behavior often results in emotional dependence, where one person relies heavily on the other for validation, comfort, and identity. This can create a sense of being emotionally trapped or overly reliant on the relationship for self-worth.
- Healthy Attachment: While there is emotional interdependence in healthy attachment, both individuals retain their independence. They feel secure in the relationship but don’t rely on the other person for everything. Healthy attachment allows for personal growth and fulfillment outside the relationship.
4. Boundaries vs. Boundary Violations
- Possessive Behavior: One hallmark of possessive behavior is the constant violation of boundaries. This may include invading personal privacy (e.g., checking personal messages or following them around) or disregarding emotional boundaries, expecting the other person to constantly prioritize their needs without regard for their own feelings.
- Healthy Attachment: Healthy attachment thrives on mutual respect for personal boundaries. Each person understands that their partner needs space and time for themselves, and there is no pressure to give up personal time or relationships in favor of the partnership. Communication about boundaries is open and respectful.
5. Reassurance vs. Security
- Possessive Behavior: A person with possessive tendencies may constantly seek reassurance from their partner, demanding verbal affirmation of love and loyalty. This need for reassurance often comes from insecurity and fear of abandonment.
- Healthy Attachment: In a healthy relationship, both partners feel emotionally secure and do not constantly seek validation. While reassurance is sometimes necessary in any relationship, it is not a frequent demand, as both individuals have faith in the strength of their bond.
The Emotional Impact of Possessive Behavior vs. Healthy Attachment
- Possessive Behavior: Over time, possessive behavior can lead to emotional burnout, anxiety, and resentment. The person being controlled may begin to feel suffocated, mistrustful, and emotionally drained. In some cases, they may even start to withdraw from the relationship in order to preserve their sense of self.
- Healthy Attachment: A healthy attachment promotes emotional well-being and satisfaction. Both individuals feel supported and valued, which leads to greater emotional resilience, trust, and fulfillment. With healthy attachment, both people feel empowered to pursue their individual goals while also strengthening their bond.
How to Foster Healthy Attachment in Your Relationships
If you find yourself leaning more toward possessive tendencies, or if you’ve noticed signs of possessiveness in your relationship, it’s important to take proactive steps to address the issue. Some strategies to foster healthy attachment and avoid possessive behavior include:
- Work on self-awareness: Recognize any tendencies to control or manipulate others and understand where they come from. Are they rooted in insecurity, fear, or past experiences? Once you acknowledge these behaviors, you can start working on healthier ways to address them.
- Open communication: Discuss your feelings with your partner honestly and calmly. Share your insecurities and listen to their perspective. Healthy communication can clear up misunderstandings and create more emotional intimacy.
- Build trust: Trust is the foundation of any healthy relationship. To build trust, be consistent in your actions, keep your promises, and be supportive of your partner’s needs. Trust also involves allowing the other person to have their own space and not expecting constant attention.
- Respect boundaries: Pay attention to your partner’s boundaries and express your own clearly. Ensure that both individuals feel comfortable and respected in the relationship.
- Develop your own identity: It’s important to nurture your own hobbies, interests, and friendships. The more confident and secure you are in your own life, the less likely you are to rely on someone else for validation.
- Seek professional help if necessary: If possessiveness or insecurity is becoming a serious issue in your relationship, it may be helpful to speak with a therapist. Professional counseling can help individuals and couples understand the root causes of possessive behavior and develop healthier relationship patterns.
Possessive Behavior in Relationships: Warning Signs
Recognizing possessive behavior in relationships can help prevent emotional distress. Some common warning signs include:
- Isolation from loved ones – A possessive partner may discourage interactions with friends or family.
- Overanalyzing social interactions – Questioning every conversation or interaction outside the relationship.
- Intense reactions to independence – Feeling threatened when a partner wants alone time or engages in solo activities.
- Controlling financial decisions – Restricting access to money or making financial choices without mutual agreement.
- Monitoring daily activities – Constantly checking a partner’s location, schedule, or interactions.
If any of these behaviors sound familiar, it may be time to seek support from a therapist for depression in NYC or an anxiety therapist NYC to develop healthier relationship dynamics and address underlying emotional concerns.
Possessive Behavior Examples
To better understand possessive behavior, let’s look at some real-life scenarios:
- Social Media Control – A partner demands access to social media accounts and insists on approving all posts or messages.
- Excessive Texting and Calling – Sending multiple messages within a short period and becoming upset when there’s no immediate response.
- Restricting Personal Choices – Insisting that a partner dresses a certain way or avoids specific activities.
- Frequent Accusations – Constantly accusing a partner of being unfaithful without any valid reason.
- Guilt-Tripping – Saying things like, “If you really loved me, you wouldn’t spend time with them.”
- Possessiveness Disguised as Protection – Making a partner feel guilty for spending time away by claiming concern for their safety.
These behaviors can escalate over time, making it crucial to address them early. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or Dialectical Behavioral Therapy can help individuals recognize and change possessive behavior tendencies.
Is There a Healthy Level of Possessiveness?
A certain level of possessiveness in relationships can be natural and even beneficial when expressed in a balanced way. Feeling a sense of attachment to your partner and wanting to spend quality time together is a sign of emotional investment. Healthy possessiveness often appears as a desire to share experiences, support one another, and maintain a strong bond. It can be a way of showing that you value your partner and the relationship.
For example, feeling a little protective when your partner is facing challenges or wanting reassurance in a relationship can be signs of care. Expressing appreciation, setting boundaries together, and prioritizing the relationship’s well-being are all positive aspects of attachment.
However, when possessiveness turns into excessive jealousy, control, or insecurity, it can become harmful. Constantly monitoring your partner’s activities, limiting their independence, or demanding constant reassurance crosses the line into unhealthy behavior. Trust and respect should always be the foundation of any relationship.
The key is balance—allowing love and care to flourish without controlling or restricting each other’s freedom. If possessiveness becomes overwhelming, seeking guidance can help develop healthier attachment patterns and strengthen emotional security.
Overcoming Possessive Behavior
If you recognize possessive behavior traits in yourself or your partner, there are ways to shift towards healthier attachment:
- Develop self-awareness – Understanding the root of insecurities can help break unhealthy patterns.
- Practice trust-building exercises – Strengthening trust through open conversations and small acts of independence can reduce possessive behavior tendencies.
- Set clear boundaries – Establishing personal space and autonomy in a relationship is essential.
- Seek professional help – A therapist for depression in NYC or anxiety therapist NYC can help address underlying fears and attachment issues.
- Engage in self-improvement – Pursuing hobbies, personal goals, and self-growth can reduce dependency on a relationship for validation.
Treatment Options for Possessive Behavior
Professional therapy can provide valuable tools for overcoming possessive behavior. Some effective treatment options include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps reframe negative thought patterns and manage jealousy.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) – Focuses on emotional regulation and mindfulness.
- Psychodynamic Therapy – Explores past experiences that contribute to possessive behavior tendencies.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) – Encourages healthy emotional responses and relationship dynamics.
- Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT) – Addresses irrational beliefs that fuel possessive behavior.
- Prolonged Exposure Therapy – Helps individuals process past traumas that may contribute to insecurity and control issues.
For those experiencing severe possessive behavior, working with a trauma therapist NYC may be beneficial in uncovering deep-seated fears and insecurities.
Finding Balance Between Love and Control
Understanding the distinction between possessive behavior and healthy attachment is key to maintaining fulfilling relationships. While possessive behavior often stems from fear and insecurity, healthy attachment is built on trust, respect, and open communication. If you or someone you know struggles with possessive behavior, seeking support from professionals at Uncover Counseling can be a vital step toward change.
By addressing the root causes of possessive behavior and fostering secure attachment styles, individuals can build relationships that are not only loving but also emotionally fulfilling and supportive. If you’re looking for guidance, our services—including relationship therapy in New York City, self-esteem therapy in NYC, stress management NYC, and anger management therapy in NYC—can help you cultivate healthier, more balanced connections. Book an appointment today.