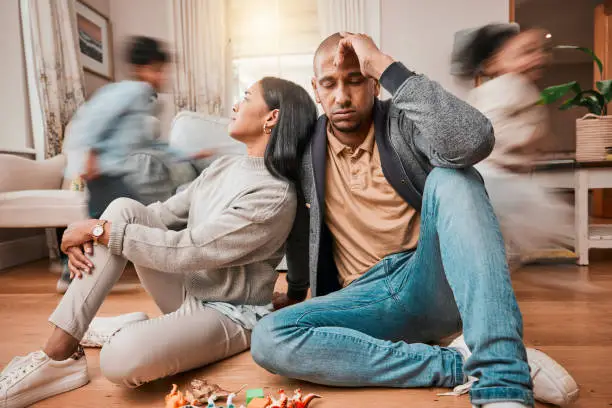
Jealousy is a natural emotion that everyone experiences at some point. However, when it becomes overwhelming, irrational, and persistent, it can develop into obsessive jealousy, which can significantly impact mental health and relationships. Unlike typical jealousy, obsessive jealousy can lead to controlling behaviors, intrusive thoughts, and even paranoia, making it a serious concern for those experiencing it and their loved ones. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help individuals regain control and maintain healthier relationships.
What Is Obsessive Jealousy?
Obsessive jealousy is an extreme form of jealousy characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts and behaviors that can negatively affect personal well-being and relationships. It often stems from deep-seated insecurities, anxiety, or past traumatic experiences. Unlike normal jealousy, which may arise occasionally in response to a specific event, obsessive jealousy is chronic and can lead to destructive patterns in relationships.
Obsessive Jealousy Disorder: When Jealousy Becomes a Mental Health Concern
Obsessive jealousy is sometimes referred to as obsessive jealousy disorder, although it is not a formal diagnosis in the DSM-5. It is often associated with underlying mental health conditions such as:
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Jealousy can become obsessive when it involves compulsive checking, questioning, or intrusive thoughts.
- Delusional Jealousy (Othello Syndrome): A psychiatric disorder where an individual has irrational beliefs that their partner is being unfaithful, despite having no evidence.
- Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): Individuals with BPD may experience intense fears of abandonment, leading to obsessive jealousy in relationships.
- Paranoid Personality Disorder: Excessive suspicion and distrust can fuel irrational jealous thoughts and behaviors.
Common Obsessive Jealousy Symptoms
Obsessive jealousy can manifest in various ways, including:
- Excessive monitoring: Constantly checking a partner’s phone, emails, or social media for signs of infidelity.
- Interrogation and accusations: Frequently questioning a partner about their whereabouts and interactions with others.
- Extreme possessiveness: Feeling threatened by any external attention given to a partner, even from friends or colleagues.
- Fear of abandonment: Intense anxiety over the possibility of losing a partner, leading to controlling behaviors.
- Compulsive reassurance-seeking: Repeatedly asking for validation that a partner is loyal and committed.
- Mood swings and anger outbursts: Becoming irritable or aggressive when jealousy is triggered.
- Self-esteem issues: Feeling unworthy or inadequate compared to perceived romantic rivals.
- Physical symptoms: Stress-related issues such as headaches, insomnia, or digestive problems due to constant worry.
Obsessive Jealousy in Relationships: The Impact on Partners
When jealousy becomes obsessive, it can create significant strain in relationships. Some consequences include:
- Emotional exhaustion: Both partners may feel drained due to constant arguments, accusations, and emotional tension.
- Erosion of trust: Instead of strengthening the relationship, obsessive jealousy can push partners apart by creating an atmosphere of suspicion.
- Controlling behavior: One partner may try to limit the other’s freedom, leading to feelings of suffocation and resentment.
- Increased conflict: Constant accusations and distrust can lead to frequent arguments and emotional distress.
- Relationship breakdown: If left untreated, obsessive jealousy can ultimately lead to the end of a relationship.
If you are experiencing challenges with obsessive jealousy in relationships, seeking Relationship Therapy in New York City can help address these issues in a constructive way.
What Personality Disorder is the Most Jealous?
Jealousy can be a significant and disruptive feature in several personality disorders, but it is particularly prominent in Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) and Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD). Although both conditions involve intense feelings of jealousy, they manifest in different ways, leading to distinct behaviors and coping mechanisms.
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is characterized by an inflated sense of self-importance, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others. Individuals with NPD often experience jealousy when they feel their status, achievements, or attention is threatened by others. This jealousy may stem from a perceived loss of superiority or recognition, especially when someone else receives the praise or attention they believe they deserve. In response, individuals with NPD may react with anger, devaluation, or attempts to undermine the person they feel jealous of. They may also become excessively possessive of their relationships, viewing their partners as extensions of themselves rather than independent individuals.
On the other hand, Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is marked by intense emotional instability, fear of abandonment, and difficulty with interpersonal relationships. For those with BPD, jealousy often arises from deep-seated insecurities and the intense fear of being abandoned or rejected by loved ones. This fear can trigger emotional outbursts, possessiveness, or desperate attempts to control the relationship. Individuals with BPD may interpret innocent actions or comments as signs of betrayal, leading to extreme jealousy and impulsive reactions.
Both NPD and BPD involve jealousy as a way to protect self-esteem or cope with emotional vulnerability, but the responses to jealousy can vary. In NPD, jealousy is often rooted in a need for validation and superiority, while in BPD, jealousy is driven by emotional fragility and fear of loss. Neither approach is optimal, as both can strain relationships and hinder healthy emotional functioning. Treatment, such as therapy, can help individuals with these disorders address underlying insecurities, improve emotional regulation, and build healthier relational patterns.
What Causes Obsessive Jealousy?
There is no single cause of obsessive jealousy, as it often stems from a combination of psychological, emotional, and environmental factors. Some common causes include:
- Insecure attachment styles: Individuals with anxious attachment may feel a heightened fear of abandonment, leading to jealous behaviors.
- Past trauma: Childhood neglect, previous relationship betrayals, or emotional abuse can contribute to deep-seated insecurities.
- Low self-esteem: Those who struggle with self-worth may feel inadequate and fear losing their partner to someone “better.”
- Unrealistic expectations: Cultural or societal norms that promote possessiveness in relationships can reinforce unhealthy jealousy patterns.
- Mental health conditions: Anxiety, depression, and personality disorders can intensify jealous tendencies.
- Substance abuse: Drug or alcohol use can exacerbate jealousy, leading to impulsive and irrational actions.
Types of Obsessive Jealousy
Obsessive jealousy refers to an irrational, overwhelming preoccupation with the fear of losing a partner or being betrayed, often resulting in intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. This type of jealousy can manifest in different forms, each with unique characteristics, but all share a common theme of intense, uncontrollable jealousy that disrupts daily life and relationships. Below are some common types of obsessive jealousy:
- Delusional Jealousy (Othello Syndrome): This form of jealousy is characterized by an unwavering, irrational belief that a partner is being unfaithful, even without any real evidence. Individuals with delusional jealousy may engage in extreme behaviors like spying, excessive questioning, and accusations. The jealousy is based on distorted perceptions rather than reality, and often leads to significant emotional distress and relationship instability.
- Pathological Jealousy: Pathological jealousy involves an intense, uncontrollable need to monitor a partner’s actions, often driven by feelings of insecurity or fear of abandonment. Individuals with this type may become obsessed with their partner’s interactions with others, constantly checking their phone, social media, or whereabouts. It can lead to controlling behaviors, such as dictating what the partner can or cannot do, where they can go, or whom they can talk to.
- Social Jealousy: Social jealousy typically manifests in a more generalized fear of being overshadowed or left behind by others. This can happen not just in romantic relationships but also in friendships or social circles. Individuals may feel inadequate or threatened by others’ successes or attention, leading to feelings of envy, possessiveness, and emotional distress.
- Reactive Jealousy: Reactive jealousy occurs when an individual responds to actual signs of infidelity or disloyalty in a relationship. While it’s often grounded in real events, the obsession and extreme responses to perceived betrayal can spiral into obsessive behaviors, such as constant questioning, accusations, or emotional outbursts.
- Romantic Obsessive Jealousy: Often stemming from deep emotional attachment and insecurity, this form of obsessive jealousy manifests as a compulsive fear of losing the partner to someone else. Individuals might fixate on small details or behaviors that they interpret as signs of infidelity, even when those signs are benign or unfounded.
Obsessive jealousy can have a devastating impact on relationships, causing emotional harm to both the individual experiencing it and their partner. Addressing obsessive jealousy often involves therapy, self-reflection, and working through underlying issues like trust, attachment, and self-esteem.
How to Overcome Obsessive Jealousy
If you or someone you love struggles with obsessive jealousy, there are several strategies that can help:
1. Identify Triggers
Recognizing what triggers jealous thoughts can help in managing them. Keeping a journal to track patterns and triggers can be useful.
2. Challenge Negative Thoughts
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can help individuals reframe irrational jealous thoughts and replace them with more balanced perspectives.
3. Develop Healthy Communication Skills
Open and honest communication with a partner can help clarify misunderstandings and reduce jealousy-induced anxiety.
4. Strengthen Self-Esteem
Building self-worth through positive affirmations, self-care, and personal development can reduce dependence on external validation.
5. Practice Mindfulness and Stress Management
Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and Stress Management NYC can help regulate emotions and prevent jealousy from spiraling out of control.
6. Set Boundaries
Establishing healthy boundaries in a relationship can foster trust and prevent controlling behaviors.
7. Seek Professional Help
If obsessive jealousy is interfering with daily life or relationships, working with a Therapist for Depression in NYC or Anxiety Therapist NYC can provide professional guidance. Various therapies such as Psychodynamic Therapy, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), and Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) can help individuals process their emotions and develop healthier coping strategies.
What Mental Illness Causes Extreme Jealousy?
Extreme jealousy, particularly when it becomes irrational, persistent, and disruptive to daily life, is often linked to various mental health conditions. In some cases, jealousy can escalate to the point of causing violent behaviors, obsessive thoughts, or even self-harm. One of the primary psychiatric conditions associated with pathological jealousy is delusional disorder – jealous type (also known as Othello syndrome). This condition is characterized by a fixed, false belief that a partner is being unfaithful, despite a lack of evidence. Individuals with this disorder may engage in compulsive behaviors such as stalking, accusations, or even aggression toward their partner or perceived rivals.
However, jealous delusions are not exclusive to delusional disorder. They can also occur in schizophrenia, where individuals may experience hallucinations or deeply ingrained paranoid beliefs, further fueling feelings of extreme jealousy. Similarly, personality disorders, such as borderline personality disorder (BPD) and narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), can contribute to excessive jealousy. People with BPD may fear abandonment and react with intense emotional outbursts, while those with NPD may feel threatened by perceived competition, leading to controlling or possessive behavior.
Additionally, anxiety disorders, particularly obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), can contribute to jealous thoughts. In some cases, individuals may experience obsessive doubts and compulsions related to their relationships, leading to persistent insecurity and distrust.
Since extreme jealousy can have serious emotional and behavioral consequences, professional treatment such as therapy, medication, and cognitive-behavioral interventions can help manage underlying mental health conditions and improve emotional regulation.
How to Support a Partner Struggling with Obsessive Jealousy
If your partner is dealing with obsessive jealousy, here are some ways to support them:
- Encourage therapy: Suggest professional help and offer emotional support during the process.
- Set clear boundaries: Make sure both partners understand what behaviors are acceptable and which are not.
- Practice patience: Recognizing that jealousy stems from deeper insecurities can help you approach the situation with compassion.
- Avoid enabling behavior: Reassuring excessively may only reinforce obsessive jealousy; instead, encourage self-reflection.
- Prioritize self-care: Being in a relationship with someone struggling with obsessive jealousy can be draining—ensure you have your own support system.
Treatment Options for Obsessive Jealousy
Various therapy approaches can help individuals manage and overcome obsessive jealousy. These include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps identify and change negative thought patterns contributing to jealousy.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores past experiences and deep-rooted emotions that may fuel jealousy.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): Focuses on emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Encourages individuals to accept their emotions while committing to healthier behavior.
- Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT): Challenges irrational jealous thoughts and replaces them with rational beliefs.
- Prolonged Exposure Therapy: Helps individuals address past trauma that may contribute to their jealousy.
Overcome Obsessive Jealousy Today
Obsessive jealousy is more than just a fleeting emotion—it can disrupt relationships, damage mental health, and lead to controlling behaviors. Recognizing obsessive jealousy symptoms, understanding its root causes, and seeking professional support can help individuals regain emotional balance and develop healthier relationships. Therapy is an effective way to work through underlying insecurities and foster trust and self-worth.
At Uncover Counseling, we provide expert mental health services to support individuals in overcoming challenges like obsessive jealousy. Whether you need help from an Anxiety Therapist NYC, Relationship Therapy in New York City, or Self-Esteem Therapy in NYC, we are here to guide you toward healing. Reach out today to start your journey toward emotional well-being and healthier relationships.