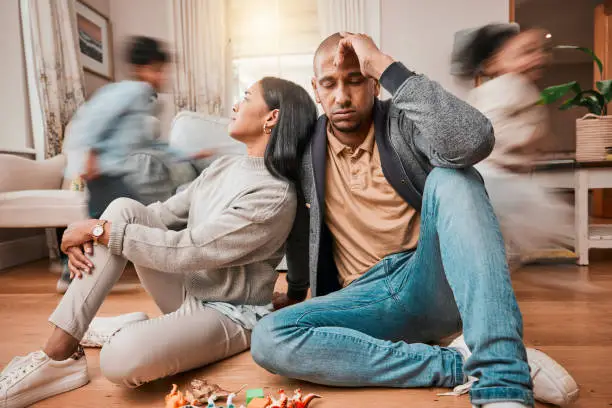
Depression is a complex mental health disorder that extends far beyond feelings of sadness or hopelessness. It impacts various aspects of a person’s life, including cognitive functions like memory. This brings us to an important question: “Can depression cause memory loss?” The answer is yes, and understanding this connection is crucial to grasping the full impact of depression on the brain. This article delves into how depression affects memory, why depression causes memory loss, and what can be done to manage these symptoms effectively. At Uncover Mental Health Counseling, we provide tailored support through professional counseling and therapeutic treatments to help individuals navigate these challenges.
Understanding Depression and Its Effects on the Brain

Depression is more than just sadness; it is a complex mental health disorder that affects millions globally. It involves a range of symptoms such as persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties, including problems with memory and concentration. These cognitive issues are often overlooked but are crucial to understanding the full impact of depression on a person’s life.
Depression affects the brain’s structure and function, particularly areas like the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory formation and retrieval. Studies have shown that depression can reduce the size of the hippocampus by up to 20%, which can lead to memory loss. The constant stress and anxiety associated with depression further exacerbate these changes. Treatments like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Psychodynamic Therapy, and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) are effective in addressing these cognitive impairments by helping patients understand and manage their symptoms.
Can Depression Cause Memory Loss?
A critical question many ask is, “Can depression cause memory loss?” The answer is a resounding yes. Depression impacts both short-term and long-term memory, affecting daily functioning. When an individual is depressed, the brain is often under constant stress. This chronic stress can interfere with the way the brain encodes and retrieves information, leading to forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, and trouble recalling past events.
Studies have demonstrated that the hippocampus, a brain region integral to forming new memories, is particularly vulnerable to the effects of depression. The repeated release of stress hormones like cortisol can shrink this region, resulting in memory problems. This is why individuals with depression often struggle with tasks that require concentration, memory retention, and recall.
It’s important to note that memory loss due to depression is not always permanent. With the right interventions, such as Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), individuals can manage these symptoms effectively and regain their cognitive functions.
Why Does Depression Cause Memory Loss?
Understanding why depression causes memory loss involves exploring the underlying neurological and psychological mechanisms. Depression affects neurotransmitter levels, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, all of which play essential roles in mood regulation and cognitive functions. When these neurotransmitters are imbalanced, it impacts not only how we feel but also how we think and remember.
Moreover, depression triggers the body’s stress response, leading to the overproduction of cortisol. While cortisol is helpful in short bursts, long-term exposure can damage the hippocampus, the brain’s memory center. This damage makes it harder for the brain to process and store new information, leading to memory difficulties. This is why depression can make even simple tasks, like remembering a friend’s name or where you left your keys, incredibly challenging.
Therapies like Prolonged Exposure Therapy and Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT) can be effective in managing depression’s cognitive effects. By addressing underlying trauma, stress, and irrational beliefs, these therapies help patients reduce avoidance behaviors and improve their ability to process and store memories.
Can Depression Cause Dementia-Like Symptoms?

Another significant concern is, “Can depression cause dementia-like symptoms?” The term “pseudo-dementia” is used to describe cognitive impairments caused by depression that mimic the symptoms of dementia. People with depression can exhibit confusion, forgetfulness, and difficulty concentrating, which closely resemble early signs of dementia. However, unlike true dementia, pseudo-dementia is reversible with appropriate treatment for depression.
Distinguishing between depression-induced cognitive decline and early dementia is vital for effective treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment plans, prolonging the suffering of those affected. Mental health professionals often use a combination of cognitive assessments, patient history, and therapeutic approaches like Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT) to differentiate between the two conditions. REBT helps patients challenge and change irrational beliefs, which can significantly improve cognitive functions.
Other Mental Health Conditions and Their Impact on Memory
While depression is a primary contributor to memory loss, it is not the only mental health condition that affects cognitive functions. Anxiety, ADHD, chronic stress, addiction, and trauma can also significantly impact memory and concentration. For instance, chronic anxiety keeps the brain in a constant state of hyper-alertness, impairing its ability to focus and retain new information. Similarly, ADHD can affect working memory, making it difficult to concentrate on tasks and remember details.
When conditions like depression and anxiety co-occur, memory problems can worsen, creating a challenging cycle to break. This is why comprehensive treatment plans that address multiple aspects of mental health are vital. At Uncover Mental Health Counseling, we offer services such as anxiety therapy, anger management, relationship therapy, and a therapist for depression to help manage these co-occurring disorders and improve cognitive functions.
Treatments like CBT, DBT, ACT, and REBT are designed to help clients develop coping strategies that manage memory loss and regain cognitive clarity by targeting the root causes of these issues.
How Depression-Related Memory Loss Affects Daily Life
The effects of memory loss due to depression extend beyond forgetting names or where you left your keys. It can significantly impact daily life, work performance, and personal relationships. People with depression-related memory loss may forget important appointments, conversations, or tasks, leading to misunderstandings and strained relationships. This can create a vicious cycle, where memory loss fuels depression, which in turn exacerbates memory loss.
In professional settings, memory loss can affect productivity, decision-making, and overall job performance. A person might struggle to complete tasks, recall important information, or make effective decisions. These challenges can lead to feelings of frustration, inadequacy, and low self-esteem, further deepening the depression.

In such cases, relationship therapy can be beneficial for couples or families trying to navigate the complexities of living with someone experiencing depression-related memory loss. Therapy focused on improving self-esteem can also be crucial in mitigating the negative impact of memory loss on daily interactions.
Managing Memory Loss Due to Depression
If you or a loved one is experiencing memory loss due to depression, there are several practical steps and strategies that can help manage and mitigate these symptoms:
- Therapy and Counseling: Engaging in evidence-based therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) can significantly improve cognitive functions. These therapies focus on changing negative thought patterns, reducing stress, and enhancing emotional regulation, all of which contribute to better memory and concentration.
- Medication: In some cases, medications like antidepressants are necessary to help balance neurotransmitters in the brain, which can improve mood and cognitive functions. A professional therapist or psychiatrist can guide you in finding the right medication and dosage tailored to your needs.
- Lifestyle Changes: Implementing lifestyle changes can also play a crucial role in managing depression-related memory loss. Regular physical exercise has been shown to boost brain health by increasing blood flow and stimulating the release of neurotransmitters that improve mood and cognitive function. A healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other brain-boosting nutrients can also help support memory and overall brain health.
- Mindfulness Practices: Incorporating mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety, which in turn improves focus and memory retention. Mindfulness techniques have been shown to increase the size of the hippocampus, counteracting the effects of depression on this critical brain region.
- Professional Support: A multi-disciplinary approach involving mental health professionals can provide comprehensive care tailored to the individual’s needs. At Uncover Mental Health Counseling, we offer various treatments like Psychodynamic Therapy, DBT, and ACT to address both memory loss and other cognitive issues caused by depression.
- Routine and Organization: Establishing a daily routine and using organizational tools like planners, reminders, and apps can help manage memory loss. Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps and setting specific goals can also improve memory retention and reduce cognitive overload.
By combining these approaches, individuals can effectively manage memory loss, improve cognitive functions, and enhance their overall quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing memory problems and suspects depression might be the cause, seeking professional support is a crucial first step. Book an appointment with Uncover Mental Health Counseling to begin your journey toward better mental health and cognitive function.
Importance of Early Intervention and Professional Support
Early intervention is vital in preventing long-term cognitive decline associated with depression. The earlier you seek help, the better the chances of reversing memory loss and improving brain function. Professional counseling and therapy can help manage both depression and its cognitive symptoms, providing tools to navigate life’s challenges.
At Uncover Mental Health Counseling, we offer a range of therapeutic approaches tailored to meet each individual’s unique needs, including CBT, ACT, DBT, and more. Don’t let depression take control of your mind—reach out for support today. Book an appointment with our experienced therapists and take the first step towards better mental health.
Understanding Memory Loss in Depression and Finding a Therapist for Depression in NYC
Depression is a complex mental health condition that can profoundly affect the brain, including causing memory loss. Understanding why depression affects memory and how to manage these symptoms is crucial for improving quality of life. With the right support, therapy, and lifestyle changes, it is possible to regain control and improve cognitive functions.
If you or someone you know is struggling with depression and memory loss, don’t wait. Professional help is available, and early intervention can make all the difference. Book an appointment with Uncover Mental Health Counseling today to start your journey to recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How can I tell if my memory loss is due to depression or something else?
A: A professional evaluation by a therapist or mental health expert can help determine whether memory loss is related to depression or another condition like dementia or anxiety.
Q2: Can therapy help improve my memory if I’m suffering from depression?
A: Yes, therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) have been shown to help improve memory and cognitive functions by addressing the root causes of depression.
Q3: Are there any medications specifically for depression-related memory loss?
A: Antidepressants can help balance neurotransmitters in the brain, which may improve memory. Consult a psychiatrist or therapist for depression to discuss the best treatment options for you