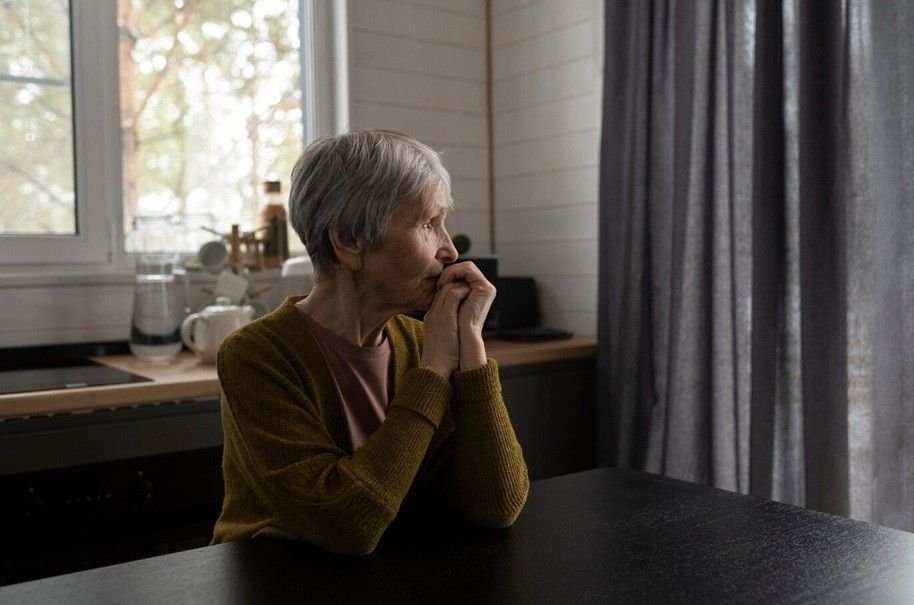
Anxiety is often perceived as a condition that primarily affects younger individuals, but it is a prevalent issue among older adults as well. Anxiety in older adults can significantly impact daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Despite its widespread nature, it often goes undiagnosed or untreated due to stigma, misattribution of symptoms to aging, or a lack of awareness. Understanding the root causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring effective treatment options are crucial in supporting older adults in managing their anxiety.
Causes of Anxiety in Older Adults

There are various factors that contribute to the development of anxiety in older adults. These can range from life transitions to underlying health conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Health-Related Concerns
Many older adults experience chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, or arthritis. These health conditions can contribute to anxiety due to physical discomfort, frequent medical visits, and uncertainty about the future. Cognitive decline, including early signs of dementia, can also be a significant source of anxiety.
2. Social Isolation and Loneliness
As people age, they may experience the loss of friends and family members, retirement, or reduced mobility, which can lead to increased isolation. The lack of social engagement is a major contributor to anxiety in older adults, as it can lead to feelings of sadness, loneliness, and helplessness. Professional senior home care services can provide companionship and emotional support, helping older adults feel more connected and less isolated.
3. Financial Stress
Many older adults live on fixed incomes, which can cause financial strain. Concerns about medical expenses, housing costs, and supporting dependents can lead to significant stress and anxiety.
4. Life Transitions
Retirement, the loss of independence, moving into assisted living facilities, or major lifestyle changes can be unsettling. Adjusting to new routines and environments can trigger anxiety, especially when coupled with other stressors.
5. Past Trauma or Unresolved Emotional Issues
Older adults may have experienced traumatic events earlier in life that continue to impact their mental health. Unresolved trauma, including past abuse, military service-related PTSD, or significant losses, can contribute to heightened anxiety levels.
What Is the 3-3-3 Rule for Anxiety?
The 3-3-3 rule for anxiety is a simple yet effective grounding technique designed to help individuals regain a sense of control and presence when experiencing overwhelming anxiety. It is especially useful in moments of acute stress, panic, or anxious thoughts, allowing individuals to redirect their focus to their immediate surroundings.
To practice the 3-3-3 rule, follow these steps:
- Identify Three Objects – Look around you and name three things you can see. These could be anything in your environment, such as a chair, a book, or a window. This step helps shift your focus away from anxious thoughts and onto tangible elements in your surroundings.
- Recognize Three Sounds – Close your eyes or focus your attention on listening for three different sounds. It could be the hum of an air conditioner, birds chirping outside, or distant traffic. This step helps ground you in the present moment by tuning into your auditory senses.
- Move Three Body Parts – Engage in small physical movements by wiggling your fingers, rolling your shoulders, or stretching your toes. This physical engagement helps release some of the built-up tension caused by anxiety and connects you back to your body.
Many people find the 3-3-3 rule useful as an immediate tool to disrupt anxious thought patterns and regain control over their emotions. While it is not a substitute for professional treatment, it can serve as a valuable coping mechanism for managing anxiety in daily life. By focusing on your surroundings and physical sensations, this technique can provide a sense of calm and stability in moments of distress.
Symptoms of Anxiety in Older Adults
Recognizing the symptoms of anxiety in older adults is essential for early intervention and treatment. While symptoms can vary, they often manifest in the following ways:
1. Physical Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Muscle tension
- Increased heart rate
- Shortness of breath
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Sleep disturbances
2. Emotional Symptoms
- Excessive worry or fear
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Feeling overwhelmed or helpless
3. Cognitive Symptoms
- Difficulty concentrating
- Racing thoughts
- Overanalyzing situations
- Forgetfulness or confusion (which can sometimes be mistaken for early dementia)
4. Behavioral Symptoms
- Avoidance of social situations
- Withdrawal from loved ones
- Repetitive behaviors or rituals
- Increased dependence on alcohol or medication to cope
If left untreated, these symptoms can significantly impact quality of life, leading to depression, physical health deterioration, and an increased risk of cognitive decline.
Impact of Anxiety on Overall Health and Well-being
Anxiety can have a significant impact on an older adult’s overall well-being. If left untreated, chronic anxiety can lead to serious health problems, including:
- Increased risk of heart disease and high blood pressure
- Weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to illness
- Higher likelihood of developing depression
- Cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia
Understanding these risks highlights the importance of addressing anxiety in older adults to ensure a healthier and more fulfilling life.
What Are the 4 C’s of Anxiety?
The 4 C’s of anxiety refer to four key psychological factors that can influence an individual’s experience of anxiety: competence, confidence, character, and connection. These elements play a significant role in shaping how we perceive and respond to stress, challenges, and uncertainty.
- Competence – This refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to handle tasks, challenges, and responsibilities effectively. When someone feels competent, they are less likely to experience anxiety because they trust their ability to manage situations. However, a lack of competence or self-doubt can lead to heightened anxiety, especially in high-pressure situations.
- Confidence – Confidence is closely tied to competence but focuses more on self-assurance and belief in oneself. Those with low confidence levels may struggle with anxiety because they second-guess their abilities or fear failure. By developing self-confidence through practice and positive reinforcement, individuals can reduce anxiety and improve their ability to face challenges.
- Character – Character encompasses personal values, integrity, and resilience. When individuals have a strong sense of character, they are more likely to feel secure in their choices and actions, reducing anxiety related to moral dilemmas or self-doubt. Those who struggle with anxiety may benefit from strengthening their sense of self and personal values.
- Connection – Social support and meaningful relationships play a crucial role in mental well-being. A strong sense of connection with others can reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common triggers for anxiety. People with strong support networks tend to manage stress more effectively, whereas those who feel disconnected may experience increased anxiety.
While caring (sometimes considered the fifth C) can positively influence emotional well-being, imbalanced or excessive caregiving can sometimes lead to anxiety. Understanding and nurturing the 4 C’s—competence, confidence, character, and connection—can help individuals develop resilience, manage anxiety more effectively, and build a stronger sense of self.
Treating Anxiety in Older Adults
There are numerous treatment approaches for treating anxiety in older adults. A combination of therapy, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, medication can be highly effective in managing anxiety.
1. Therapy and Counseling
Seeking professional support is one of the most effective ways to manage anxiety. At Uncover Counseling, we offer various therapeutic services that can help older adults navigate their anxiety, including:
Specific therapy approaches that have proven effective for anxiety in older adults include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals identify and reframe negative thought patterns.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Focuses on past experiences and unresolved conflicts that may contribute to anxiety.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): Incorporates mindfulness and distress tolerance techniques to manage emotions.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Encourages individuals to embrace their thoughts and feelings rather than fighting them.
- Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT): Focuses on identifying irrational beliefs that fuel anxiety.
- Prolonged Exposure Therapy: Beneficial for individuals with PTSD-related anxiety.
2. Medication: When is it Necessary?
In some cases, medication may be recommended alongside therapy. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are commonly prescribed for anxiety. However, medication should always be used under medical supervision, particularly in older adults who may have multiple prescriptions for other health conditions.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in managing anxiety. These include:
- Regular Exercise: Walking, yoga, or gentle stretching can help reduce stress levels.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and hydration can improve overall well-being.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding stimulants before bedtime can improve sleep quality.
- Social Engagement: Maintaining social connections through clubs, volunteer work, or regular visits with loved ones can reduce feelings of isolation.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practicing meditation, deep breathing, or progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the nervous system.
4. Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation practices can help older adults manage stress and anxiety. Some effective techniques include:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practicing controlled breathing can calm the nervous system.
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Engaging in meditation can promote a sense of peace and clarity.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tensing and relaxing different muscle groups can reduce physical tension and anxiety.
5. Social Support
Having a strong support system is essential for reducing anxiety. Encouraging older adults to stay connected with friends and family can improve their emotional well-being. Participating in community activities, joining senior centers, and engaging in hobbies can provide a sense of purpose and prevent isolation.
What Foods Are Good for Anxiety in Adults?
Diet plays a crucial role in mental well-being, and certain foods can help reduce anxiety levels by stabilizing blood sugar, supporting brain function, and promoting relaxation. One of the best dietary approaches for managing anxiety is incorporating complex carbohydrates, which provide a steady release of energy and help regulate mood.
1. Eat Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates have a calming effect on the body by increasing serotonin production, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and emotional stability. Unlike simple carbohydrates, which can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, complex carbs offer long-lasting energy and improved mood stability. Some of the best sources include:
- Oatmeal – A great breakfast option that helps maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Quinoa – A nutrient-dense grain that provides essential amino acids for brain health.
- Whole-Grain Breads and Cereals – These support a balanced diet and prevent energy fluctuations that can worsen anxiety.
2. Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Foods rich in omega-3s, such as salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, help reduce inflammation and support brain function. Studies suggest that omega-3s can lower cortisol levels (the stress hormone) and promote relaxation.
3. Choose Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium plays a vital role in calming the nervous system and preventing stress-related symptoms. Some excellent sources include:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Almonds and cashews
- Pumpkin seeds
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
4. Consume Foods High in B Vitamins
B vitamins help regulate mood and reduce stress, making them essential for anxiety management. Foods rich in B vitamins include:
- Eggs
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans)
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey)
- Nutritional yeast
5. Stay Hydrated and Limit Caffeine & Sugar
Dehydration can worsen anxiety symptoms, so drinking plenty of water is essential. Additionally, limiting caffeine and sugary foods can prevent energy crashes and nervousness, which may exacerbate anxiety.
By prioritizing nutrient-dense foods and avoiding processed sugars and simple carbs, adults can create a diet that supports mental clarity, relaxation, and emotional balance. A well-rounded, healthy diet can complement therapy and other anxiety management techniques to improve overall well-being.
Additional Coping Strategies

1. Engaging in Meaningful Activities
Engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy can significantly reduce anxiety. Activities such as painting, gardening, reading, and volunteering provide a sense of accomplishment and help seniors stay mentally engaged.
2. Limiting News and Media Consumption
Excessive exposure to negative news can heighten anxiety. Encouraging older adults to limit their media consumption and focus on positive content can help reduce unnecessary stress and worry.
3. Practicing Gratitude and Positive Thinking
Journaling about positive experiences, expressing gratitude, and focusing on the present can shift attention away from anxious thoughts and promote a more positive outlook on life.
Overcoming Anxiety in Older Adults
Anxiety in older adults is a serious but manageable condition. By understanding the causes of anxiety in older adults, recognizing the symptoms of anxiety in older adults, and exploring effective treatment options, individuals can regain control of their mental well-being. Seeking professional support, making lifestyle changes, and engaging in therapeutic interventions are crucial steps toward improving quality of life.
At Uncover Counseling, we offer specialized services to help individuals navigate anxiety, stress, and other mental health challenges. Whether through Anxiety Therapy, CBT, DBT, or Stress Management, our team is here to provide compassionate, evidence-based care. If you or a loved one is struggling with anxiety, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional support. By raising awareness and fostering open conversations about mental health, we can help ensure that older adults receive the care and attention they deserve. Book an appointment today.