Mental health is complex, and as we continue to learn more about various psychological conditions, new terms and concepts emerge. One such concept is borderpolar. Although not officially recognized as a distinct disorder in many diagnostic systems, the term has been gaining attention in mental health circles, particularly about conditions like Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Bipolar Disorder. Understanding what borderpolar means, how it manifests, and its impact on emotional regulation and behavior is essential for those who may be struggling with symptoms of this condition. In this article, we’ll explore borderpolar, its relationship to other disorders, and provide insights into managing symptoms effectively.

What is Borderpolar? Understanding the Term and Its Origins
Borderpolar is a relatively new term that is used to describe a mental health condition that shares features of both Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Bipolar Disorder. The term itself is a blend of the two, reflecting the overlap in symptoms, particularly regarding mood swings, emotional regulation, and interpersonal challenges. People with borderpolar may experience rapid shifts between moods, emotional instability, and impulsive behavior, which can make relationships and daily functioning difficult.
The term originated from informal discussions within the mental health community as a way to capture the intersection of these two complex disorders. While borderpolar is not yet an officially recognized diagnosis, it represents a spectrum of symptoms that are commonly seen in individuals who struggle with both emotional regulation and mood disorders. Understanding borderpolar requires recognizing its ties to both BPD and Bipolar Disorder, as well as acknowledging the potential challenges in diagnosing and treating the condition.
The Difference Between Borderpolar and Borderline Personality Disorder
To better understand borderpolar, it’s important to first look at the primary components: Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Bipolar Disorder. BPD is characterized by intense emotional reactions, unstable relationships, a fear of abandonment, and difficulty regulating emotions. Individuals with BPD may experience extreme mood swings, but these tend to be more related to external events, such as interpersonal conflicts or feelings of rejection.
On the other hand, Bipolar Disorder is characterized by extreme mood fluctuations that cycle between manic or hypomanic episodes (elevated or irritable mood) and depressive episodes (low mood). These mood shifts are less influenced by external events and more by internal biochemical changes in the brain.
Borderpolar shares characteristics of both these conditions, such as rapid mood changes, emotional instability, impulsive behavior, and interpersonal difficulties. However, while BPD is primarily focused on emotional instability in the context of relationships, and Bipolar Disorder centers on mood swings, borderpolar represents a hybrid of these two, resulting in overlapping symptoms.
When someone with borderpolar experiences a mood swing, it can be a combination of the extreme highs associated with mania and the lows seen in depression, as well as the intense emotional reactions characteristic of BPD.
What Happens if You Have Both Borderpolar and BPD?
Having both borderpolar and Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) can significantly complicate the clinical course of Bipolar Disorder (BD). Studies indicate that comorbid BPD tends to worsen the prognosis for individuals with BD, creating an unfavorable illness trajectory. People with both conditions may experience earlier onset of mood symptoms, making it more difficult to manage and predict mood episodes.
Additionally, individuals with borderpolar and BPD are more likely to require hospitalization due to the severity of their symptoms, which can include emotional instability, impulsivity, and difficulty regulating moods. The treatment duration may be longer, as the presence of BPD can interfere with the effectiveness of typical treatments for BD. Patients with both conditions often have a worse response to standard treatments, necessitating a more tailored approach that combines mood stabilization strategies with therapies specifically targeting emotional regulation and interpersonal challenges. Proper treatment is crucial to improve outcomes and manage symptoms.
Why is Borderline Personality Disorder So Hard to Live With?
Living with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) can be challenging due to the intense mood swings and uncertainty about one’s identity. Individuals with BPD often experience rapid shifts in how they view themselves, leading to confusion and instability. Their emotions toward others can change drastically, swinging from extreme closeness to extreme dislike, often without clear reasons. These unpredictable emotional changes can result in unstable relationships, creating a sense of emotional turmoil. The constant flux in feelings and self-image can cause significant distress, making it difficult to maintain balance in daily life. For those with BPD, the emotional pain from these struggles can feel overwhelming.
How Borderpolar Affects Emotional Regulation and Behavior
The emotional regulation difficulties experienced by individuals with borderpolar can significantly affect their behavior and decision-making. Emotional regulation refers to the ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences in a healthy and constructive way. People with borderpolar may find it difficult to control their emotions, leading to outbursts, impulsivity, and self-destructive behavior.
During the depressive phase, individuals may feel hopeless, worthless, and withdrawn, making it hard to engage in daily tasks or maintain relationships. On the flip side, during the manic or hypomanic phases, they may experience extreme highs, where they feel invincible, impulsive, and reckless. These mood swings can create a chaotic internal world and make it difficult to maintain stability in relationships or professional settings.
Because emotional regulation is a core feature of borderpolar, managing intense feelings can be challenging. Individuals may struggle with fluctuating self-esteem, impulsive decisions, and even self-harm as a way of coping with emotional distress.
Signs and Symptoms of Borderpolar in Mental Health
Borderpolar symptoms often resemble those of both Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Bipolar Disorder, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment. Some common signs of borderpolar include:
- Mood swings: Extreme fluctuations between depression and mania or hypomania, often without clear triggers, can be one of the most noticeable symptoms.
- Emotional instability: Individuals may experience intense emotional reactions, leading to rapid and unpredictable changes in mood.
- Impulsivity: People with borderpolar may engage in risky behaviors, such as reckless spending, unsafe sexual activity, or substance use.
- Interpersonal difficulties: Emotional volatility can make relationships challenging, with fear of abandonment and an unstable self-image often leading to conflict or withdrawal.
- Feelings of emptiness: A persistent sense of emptiness or dissatisfaction with life can contribute to self-destructive behaviors.
- Inconsistent self-esteem: A fluctuating sense of self-worth can swing dramatically, making it hard to maintain stable views of oneself.
These symptoms can cause significant distress in daily life, making it essential to understand how emotional regulation and behavior relate to mental health. Recognizing the signs of borderpolar can help individuals seek the appropriate support and treatment for improved well-being.
How to Treat Borderpolars?
Treating borderpolar requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach, as the symptoms overlap with both Bipolar Disorder (BD) and Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD). Effective treatment combines pharmacotherapy, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to address the complexity of the condition.
- Pharmacotherapy: Medications play a key role in managing borderpolar symptoms. Mood stabilizers such as lithium, valproate, or lamotrigine can help control the extreme mood swings associated with BD, while antipsychotic medications like aripiprazole or quetiapine may help reduce emotional instability. In some cases, antidepressants can be used to alleviate symptoms of depression, though they must be prescribed carefully to avoid triggering manic episodes.
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) are commonly used for treating borderpolar. CBT helps individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns, while DBT is specifically designed to address emotional regulation and interpersonal challenges. Both therapies aim to help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and improve emotional stability.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Consistent routines, proper sleep hygiene, and stress management techniques like mindfulness can significantly help reduce mood fluctuations and support emotional regulation.
Overall, the combination of pharmacotherapy and therapy, along with a healthy lifestyle, is essential for managing borderpolar symptoms and improving quality of life.
The Role of Trauma and Environmental Factors in Borderpolar Development
Trauma and environmental factors play a significant role in the development of mental health disorders, including borderpolar. Early childhood trauma, neglect, or abuse can contribute to the development of emotional regulation difficulties, which are core to both BPD and Bipolar Disorder. Additionally, environmental stressors such as family dysfunction, substance abuse, or chronic stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Trauma, particularly attachment trauma or experiences of abandonment, can make it difficult for individuals with borderpolar to form stable relationships or maintain a consistent sense of self. Over time, this can contribute to the mood instability seen in borderpolar disorder.
The Challenges of Diagnosing Borderpolar and Its Impact on Treatment
Diagnosing borderpolar can be challenging due to its overlap with other disorders. Professionals may initially misdiagnose someone with either BPD or Bipolar Disorder, leading to delayed treatment or inappropriate interventions. The symptoms of borderpolar can be fluid and may change over time, making it difficult to pinpoint a definitive diagnosis.
The complexity of borderpolar often means that individuals will require a nuanced and multi-faceted treatment approach. Addressing both the emotional instability of BPD and the mood fluctuations of Bipolar Disorder is key to managing the condition effectively.
Coping Strategies for Managing Borderpolar Symptoms
Managing borderpolar symptoms involves developing emotional regulation skills, self-awareness, and effective coping strategies. Here are some helpful techniques:
- Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness helps individuals become more aware of their emotions and creates a space between feeling and action. This can reduce impulsivity and increase emotional stability, allowing for more controlled responses to triggers.
- Grounding exercises: Grounding techniques, such as deep breathing or sensory awareness, can help individuals stay calm and present when experiencing emotional turmoil. These exercises are essential in diffusing overwhelming feelings.
- Structured routines: Maintaining a consistent daily routine for sleep, meals, and self-care provides stability, which can help reduce mood fluctuations. Structure can promote emotional balance and reduce feelings of chaos.
- Journaling: Writing in a journal can help individuals track their emotions, triggers, and behaviors. This practice encourages self-reflection and helps recognize patterns, which can be useful for managing emotional responses and preventing impulsivity.
By incorporating these coping strategies, individuals with borderpolar can better manage their symptoms, improve emotional regulation, and lead more balanced lives. Consistent use of these techniques can enhance self-awareness and reduce emotional distress.
Therapeutic Approaches for Treating Borderpolar: Effective Techniques
There are several therapeutic approaches that can help individuals with borderpolar manage their symptoms:
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): DBT is particularly effective for individuals with BPD and borderpolar. It helps individuals regulate their emotions and develop healthier coping strategies.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, which can be helpful for individuals with borderpolar who experience mood swings.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: This therapy helps individuals explore the root causes of their emotional instability and gain insight into their behaviors and relationships.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT helps individuals accept difficult emotions while committing to behaviors that align with their values, helping to reduce emotional distress.
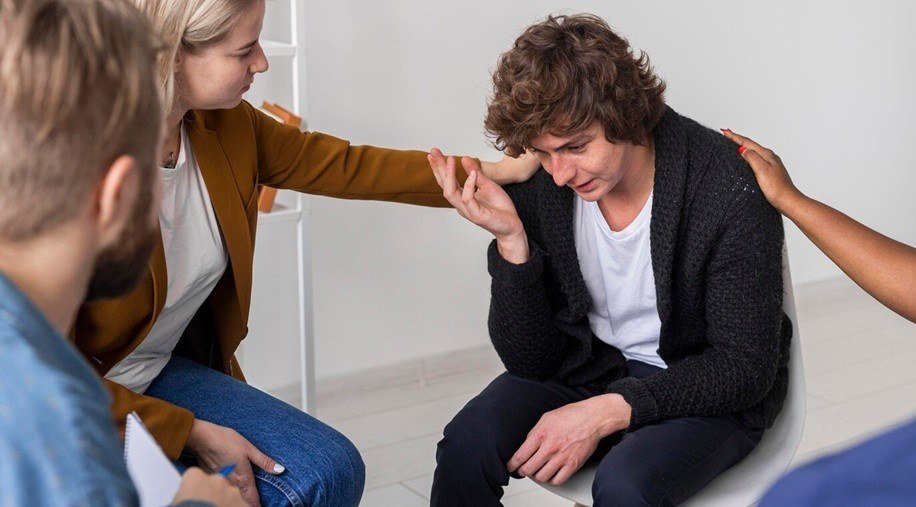

The Importance of Support Systems in Managing Borderpolar
A strong support system is vital for individuals dealing with borderpolar. Support from family, friends, and mental health professionals can provide the encouragement and validation needed to navigate emotional challenges. Support groups, in particular, can help individuals connect with others who understand their struggles and offer valuable coping strategies.
When to Seek Professional Help for Borderpolar
If you or someone you know is experiencing the symptoms of borderpolar, it’s important to seek professional help. A qualified therapist can conduct a thorough evaluation, provide a diagnosis, and recommend a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention can improve outcomes and help individuals lead more stable and fulfilling lives.
At Uncover Counseling, we offer comprehensive services to support individuals with mental health challenges, including anxiety therapy, depression treatment, and trauma therapy.
Understanding Borderpolar and Its Long-term Effects on Mental Health
Borderpolar represents a complex intersection of emotional instability and mood swings, drawing from both Borderline Personality Disorder and Bipolar Disorder. While not an official diagnosis, understanding borderpolar is crucial for managing its symptoms and improving overall mental health. With appropriate therapeutic approaches, coping strategies, and a supportive environment, individuals with borderpolar can find ways to live more balanced and fulfilling lives.If you or someone you know is struggling with symptoms of borderpolar, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Uncover Counseling offers a range of therapies to help individuals manage emotional challenges and improve their mental well-being. Book an appointment today.