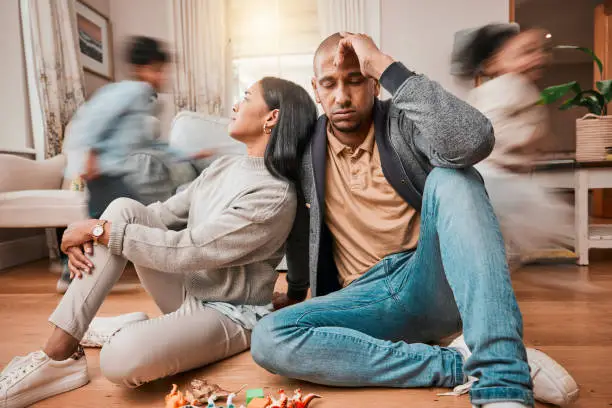
In any relationship, emotional reactivity can play a significant role in shaping how partners interact with each other. While emotional responses are natural and part of the human experience, emotional reactivity can become problematic when it leads to impulsive behaviors, misunderstandings, and unnecessary conflict. Whether it manifests as defensiveness, anger, or overwhelming sadness, emotional reactivity can negatively impact relationships and emotional well-being.
Understanding emotional reactivity, its underlying causes, and how to manage it can be key to building healthier and more fulfilling relationships. In this blog post, we’ll dive deeper into what emotional reactivity is, how it affects relationships, and provide actionable strategies for managing reactive emotions. We’ll also discuss professional treatment options for those who may need extra support, such as Anxiety Therapy in NYC, Relationship Therapy in New York City, and Self-esteem therapy in NYC with the help of the experts from Uncover Mental Health Counseling.
What is Emotional Reactivity?

Emotional reactivity refers to automatic, often intense emotional responses triggered by external stimuli. These responses are usually immediate, disproportionate, and sometimes out of sync with the situation at hand. Emotional reactivity can cause an individual to react impulsively without pausing to think about the consequences of their actions. When it comes to relationships, these reactions might include overreacting to small irritations, making accusations, or withdrawing emotionally during a disagreement.
Emotional reactivity can be the result of underlying issues like past trauma, chronic stress, or anxiety. It can also stem from deep-seated beliefs, emotional insecurities, or a lack of emotional regulation skills. In relationships, emotional reactivity can lead to heightened conflict, breakdowns in communication, and emotional disconnection. However, once you understand emotional reactivity and its triggers, you can work on addressing it and fostering more positive interactions.
Emotional Reactivity vs. Emotional Sensitivity
It’s essential to differentiate between emotional reactivity and emotional sensitivity. While both involve emotional responses, emotional reactivity is more about the intensity and automatic nature of the response. Emotional sensitivity, on the other hand, is about being attuned to others’ feelings and having a heightened sense of empathy. Emotional reactivity tends to lead to defensive or reactive behaviors, whereas emotional sensitivity is about being able to understand and support your partner’s emotional state.
Someone who is emotionally reactive might react impulsively to their partner’s criticism or become angry over minor inconveniences. In contrast, an emotionally sensitive person might be more attuned to how their partner feels but won’t necessarily react in ways that escalate the situation. Emotional reactivity is often linked to emotional dysregulation, where emotions are felt intensely and without the ability to pause and process them before reacting.
Causes of Emotional Reactivity in Relationships
Emotional reactivity in relationships doesn’t occur in a vacuum—it’s often the result of a combination of internal and external factors. Understanding these causes can be the first step toward addressing emotional reactivity and fostering healthier dynamics. Here are some of the most common causes:
1. Past Trauma or Unresolved Emotional Wounds
Trauma from childhood or previous relationships can leave deep emotional scars. These past wounds often lead to hypersensitivity to certain triggers, causing an individual to overreact in situations that remind them of the past. For example, someone who experienced abandonment or emotional neglect as a child might react intensely to perceived rejection from their partner, even if the situation doesn’t warrant such a reaction.
Trauma-based emotional reactivity is often characterized by heightened fear, anxiety, or anger, making it difficult for individuals to remain calm in situations where they feel emotionally threatened. This form of reactivity is often linked to Trauma Therapy in NYC, where individuals can work through their past experiences in a safe and supportive environment.
2. Chronic Stress and Overwhelm
When stress levels are consistently high, individuals may find it harder to regulate their emotions. Chronic stress from work, family responsibilities, or financial issues can contribute to emotional exhaustion, which lowers one’s ability to respond calmly and thoughtfully to challenging situations. In these moments, emotional reactivity may arise as a way to cope with the emotional overload.
People who are chronically stressed may find themselves snapping at their partners or becoming easily frustrated, even over minor disagreements. In these instances, stress management techniques and therapies, such as Stress Management NYC, can be particularly helpful in building emotional resilience and reducing reactivity.
3. Mental Health Conditions
Conditions like anxiety, depression, and ADHD can also contribute to emotional reactivity in relationships. For example, someone with anxiety may overreact to a partner’s comment or action out of fear or insecurity. In contrast, depression can lead to emotional withdrawal or a tendency to interpret situations in a negative light, causing a person to respond with feelings of hopelessness or anger.
Therapy can be particularly beneficial for those struggling with mental health conditions, offering tools to address the root causes of emotional reactivity. CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy) and DBT (Dialectical Behavioral Therapy) can be effective therapies for managing emotional dysregulation caused by mental health conditions.
4. Attachment Style
Your attachment style, formed in early childhood, can influence how you react in relationships. Those with insecure attachment styles—especially anxious attachment—may find themselves more emotionally reactive when they perceive a threat to their connection with their partner. For example, a person with an anxious attachment style might respond intensely to feelings of abandonment or when their partner seems distant.
Insecure attachment styles can be addressed through Relationship Therapy in New York City, which helps individuals develop healthier communication skills and emotional security in their relationships.
5. Poor Emotional Regulation Skills
Emotional reactivity often stems from a lack of emotional regulation skills. Individuals who struggle with regulating their emotions may have difficulty managing intense feelings, which leads to impulsive reactions. Learning emotional regulation skills can help individuals respond to emotional triggers in a more balanced and thoughtful manner.
Therapies like DBT are specifically designed to teach emotional regulation skills, including mindfulness techniques and distress tolerance strategies, which can reduce emotional reactivity and improve relationship dynamics.
The Impact of Emotional Reactivity on Relationships
When emotional reactivity becomes a pattern, it can have a profound effect on the health of a relationship. Here are some of the most common impacts:
1. Increased Conflict
When emotional reactivity is at play, conflicts tend to escalate rather than resolve. This is because emotionally reactive individuals often respond with defensiveness, anger, or frustration, rather than engaging in calm and constructive dialogue. This escalation can create a cycle of tension, making it harder for both partners to find common ground.
2. Emotional Disconnection
Over time, emotional reactivity can lead to emotional disconnection between partners. As conflicts intensify and trust erodes, one or both partners may begin to emotionally withdraw from the relationship. This emotional distance can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
3. Undermined Communication
When emotions are running high, effective communication becomes nearly impossible. Emotional reactivity often prevents individuals from listening to their partner’s perspective or expressing their own feelings in a productive way. This can result in misunderstandings, unmet needs, and unresolved issues.
4. Decreased Self-Esteem
Frequent emotional outbursts or harsh reactions can also damage an individual’s self-esteem, especially if they feel that they’re unable to manage their emotions in a healthy way. Additionally, being on the receiving end of emotional reactivity can cause the other partner to feel unloved or unimportant, which can further erode their self-worth.
How to Be Less Reactive: Managing Emotional Reactivity
Reducing emotional reactivity in relationships requires a combination of self-awareness, emotional regulation, and open communication. Emotional reactivity can lead to misunderstandings, conflict, and emotional distance. By implementing strategies to manage it, you can foster healthier, more balanced interactions with your partner. Here are some ways to become less emotionally reactive:
Practice Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the first step in managing emotional reactivity. Pay attention to your emotional triggers and physical sensations when you’re about to react. What sets you off? How does your body feel when you’re emotionally triggered? Recognizing the signs early on gives you the opportunity to pause before reacting impulsively. By becoming more aware of your emotional patterns, you can create space between the stimulus and your response.
Take a Timeout
Sometimes, the best thing you can do is take a break from a heated situation. Stepping away from the moment allows you to cool down, regain composure, and collect your thoughts. This timeout can help you return to the situation with a calmer, more rational mindset, which reduces the chances of an emotionally reactive response.
Use Mindfulness Techniques
Mindfulness is an effective tool for managing emotional reactivity. By practicing mindfulness, you can observe your emotions without judgment and avoid reacting impulsively. Techniques like deep breathing, focusing on the present moment, or simply taking a few seconds to pause before responding can help you gain control over your emotions. Over time, mindfulness can increase your emotional resilience and reduce reactivity.
Communicate Calmly and Assertively
How you express your emotions is key to reducing reactivity. Instead of raising your voice or becoming defensive, use “I” statements to communicate your feelings. For example, say “I feel upset when…” instead of blaming your partner. This helps you express your emotions in a calm and assertive manner without escalating the situation. Clear, open communication builds understanding and helps both partners feel heard.
Seek Professional Support
If emotional reactivity continues to create tension in your relationship, seeking professional help can provide valuable insights and tools for managing your emotions. Therapy can help you address the underlying causes of emotional reactivity, improve communication skills, and develop healthier ways of relating to your partner.
By practicing these strategies, you can take control of your emotional responses and build stronger, more harmonious relationships.
Treatments for Emotional Reactivity
Several therapeutic approaches can help individuals manage emotional reactivity. Here are some of the most effective treatments:
1. Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy helps individuals explore unconscious emotions and unresolved issues from the past. This type of therapy is useful for those who have experienced trauma or have deep-seated emotional wounds that contribute to emotional reactivity.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is an evidence-based therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns that contribute to emotional reactivity. Through CBT, individuals can learn how to challenge distorted thinking and develop more balanced emotional responses.
3. Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
DBT focuses on teaching emotional regulation skills, mindfulness, and distress tolerance. This approach is particularly helpful for those struggling with intense emotions and impulsive reactions, helping individuals manage reactivity more effectively.
4. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy helps individuals accept their emotions without judgment and commit to behaviors that align with their values. This therapy helps reduce emotional reactivity by focusing on living a meaningful life, even in the presence of difficult emotions.
5. Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT)
REBT is a type of cognitive therapy that focuses on challenging irrational beliefs and assumptions that lead to emotional overreactions. By addressing these beliefs, individuals can reduce emotional reactivity and respond to situations more rationally.
6. Prolonged Exposure Therapy
Prolonged exposure therapy is particularly helpful for individuals whose emotional reactivity stems from trauma. This therapy helps individuals process traumatic memories and reduce the emotional intensity of their responses to triggers.
Managing Emotional Reactivity for Healthier Relationships
Emotional reactivity can create significant challenges in relationships, leading to conflict, emotional disconnection, and even diminished self-esteem. However, understanding the causes of emotional reactivity and applying strategies to manage it can help individuals create healthier, more fulfilling connections with their partners.
By practicing mindfulness, improving communication skills, and seeking professional help when needed, individuals can reduce emotional reactivity and build more resilient relationships. Whether through relationship therapy, anxiety therapy, or trauma-focused therapies, there are resources available to help individuals navigate the complexities of emotional reactivity and improve their overall well-being. Taking steps to manage emotional reactivity is not only beneficial for relationships but also for personal growth and emotional health. Through consistent effort and support, individuals can learn to respond thoughtfully, cultivate emotional intelligence, and foster deeper, more meaningful connections with those they care about. Trust Uncover Mental Health Counseling, and book an appointment today.