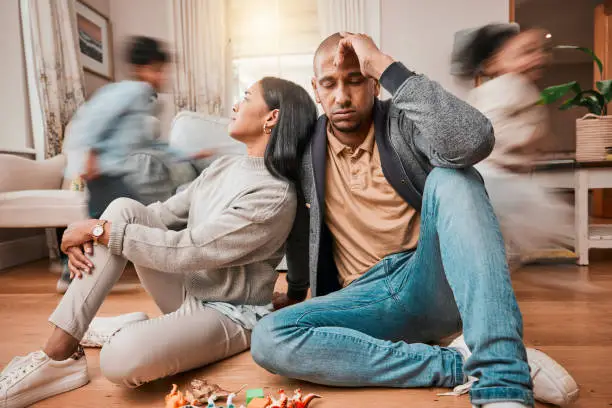
Suicidal thoughts can be overwhelming and distressing, but they do not have to define your future. If you are struggling, know that you are not alone, and help is available. Learning how to stop suicidal thoughts involves understanding their triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and seeking professional support. With the right strategies and assistance, it is possible to regain hope and work toward healing. This article will explore how to deal with suicidal thoughts, differentiate between passive suicidal thoughts and active ideation, and discuss how to cope with suicidal thoughts effectively. If you or someone you know is struggling, professional support is available at Uncover Counseling.
Understanding Suicidal Thoughts
Suicidal thoughts can manifest in various ways and may stem from deep emotional pain, unresolved trauma, or overwhelming stress. Understanding the root causes and different types of suicidal ideation is an essential step toward healing and seeking the right support.
What Causes Suicidal Thoughts?
Several factors can contribute to suicidal thoughts, including:
- Mental Health Disorders – Conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and bipolar disorder can increase vulnerability to suicidal ideation.
- Past Trauma and Abuse – Experiencing childhood abuse, domestic violence, or the loss of a loved one can lead to emotional distress and hopelessness.
- Chronic Stress and Life Pressures – Financial problems, work-related burnout, or relationship conflicts can cause significant emotional strain.
- Social Isolation and Loneliness – A lack of meaningful connections or support systems can increase feelings of despair.
- Substance Abuse – The misuse of drugs or alcohol can intensify negative emotions and lead to impulsive thoughts.
- Chronic Health Conditions – Living with long-term pain or a debilitating illness can contribute to suicidal ideation.
Passive vs. Active Suicidal Thoughts
It’s important to differentiate between the two main types of suicidal thoughts:
- Passive Suicidal Thoughts – These involve a desire to escape life or wishing for death without making specific plans to end one’s life.
- Active Suicidal Thoughts – These include concrete plans or intent to carry out self-harm.
Recognizing the difference can help individuals and their loved ones seek appropriate intervention. If you or someone you know is struggling, professional support from a qualified therapist can provide the necessary guidance and tools to navigate these thoughts and find hope again.
What Are the Main Causes of Suicidal Thoughts?
Suicidal thoughts can arise from various personal, emotional, and psychological challenges. While each person’s experience is unique, several common factors contribute to suicidal ideation. These feelings often stem from overwhelming distress, feelings of hopelessness, or an inability to see a way forward. Below are some of the most frequent causes of suicidal thoughts:
1. Mental Health Conditions
Mental health disorders play a significant role in the development of suicidal ideation. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can intensify feelings of despair, making it difficult to cope with daily life. When untreated, these conditions can make individuals feel trapped in their emotional pain.
2. Bullying, Prejudice, and Social Stigma
Experiencing discrimination or social rejection based on race, gender identity, sexual orientation, disability, or cultural background can lead to deep emotional distress. Bullying—whether in person or online—can significantly impact self-esteem and contribute to feelings of isolation, self-doubt, and unworthiness, all of which may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts.
3. Experiencing Different Forms of Abuse
Exposure to abuse, whether physical, emotional, sexual, or domestic, can have long-term psychological effects. Survivors of abuse may struggle with feelings of shame, guilt, and self-blame, leading to suicidal ideation. Without proper support, these experiences can create lasting emotional wounds.
4. Grief and Loss
The death of a loved one, especially due to suicide, can lead to immense emotional pain and deep feelings of emptiness. Bereavement can leave individuals struggling to find meaning in life, increasing the risk of suicidal thoughts.
5. Relationship Breakdowns
The end of a significant relationship—whether due to divorce, separation, or an unexpected breakup—can cause feelings of abandonment and hopelessness. The emotional turmoil of losing someone important can sometimes make it difficult to imagine a future without them.
Understanding these common causes of suicidal thoughts is essential in identifying when help is needed. Seeking therapy, building a support system, and reaching out to loved ones can provide hope and guidance during difficult times. If you or someone you know is struggling, professional help is available. You are not alone, and support is within reach.
How to Deal with Suicidal Thoughts: Immediate Steps to Take
If you are experiencing suicidal thoughts, consider the following immediate actions on how to stop suicidal thoughts:
1. Reach Out for Support
- Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or therapist.
- Call a crisis helpline or seek emergency assistance if needed.
2. Remove Immediate Risks
- If you have access to means of self-harm, consider giving them to someone trustworthy or creating a safe environment.
3. Distract Yourself
- Engage in activities that require focus, such as reading, exercising, or listening to music.
- Try grounding techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation.
4. Challenge Negative Thoughts
- Recognize that thoughts of suicide do not define reality.
- Practice self-compassion and remind yourself that feelings are temporary.
5. Create a Safety Plan
- List emergency contacts and coping strategies.
- Identify reasons to live and revisit them in difficult moments.
What Are Five Signs That a Person May Be Depressed and Suicidal?
Recognizing the warning signs of depression and suicidal thoughts is crucial in providing timely support and intervention. While the symptoms may vary from person to person, there are common behavioral and emotional changes that can indicate someone is struggling. If you notice any of these signs in yourself or someone you know, it’s important to seek help and offer support.
1. Making a Plan or Researching Ways to Die
One of the most serious warning signs of suicidal intent is when a person begins making concrete plans to end their life. This may include searching online for methods of self-harm, acquiring potentially harmful objects, or expressing a desire to no longer be alive. If someone talks about wanting to die or makes statements such as, “I can’t do this anymore,” it should be taken very seriously.
2. Withdrawing from Friends and Family
A person experiencing depression and suicidal thoughts may begin to isolate themselves from loved ones. They may stop responding to messages, decline social invitations, or appear emotionally detached. Additionally, some individuals may say goodbye to friends or family members in an unusual way, give away personal belongings, or even create a will—suggesting they are preparing for the possibility of ending their life.
3. Taking Dangerous Risks
Engaging in reckless or self-destructive behaviors can be an indirect sign of suicidal ideation. This might include driving at dangerously high speeds, engaging in unsafe sexual activity, or putting themselves in harm’s way without concern for the consequences. Increased impulsivity and risk-taking behavior can indicate a loss of interest in personal safety and well-being.
4. Displaying Extreme Mood Swings
A person struggling with suicidal thoughts may exhibit noticeable and unpredictable mood swings. They may go from deep sadness and despair to bursts of anger or sudden moments of euphoria. In some cases, an unexpected sense of calm after a prolonged period of depression may signal that they have made the decision to end their life.
5. Changes in Sleep, Appetite, or Substance Use
Depression often affects sleep patterns and eating habits. Some people may experience insomnia, while others may sleep excessively. Similarly, changes in appetite—either eating too much or too little—can be a sign of emotional distress. Additionally, increased use of drugs or alcohol can be a way for someone to numb their pain or escape their thoughts, further increasing their risk of suicide.
Recognizing these warning signs is the first step in preventing a tragedy. If you or someone you know is displaying these behaviors, reaching out for professional help is essential. Support from mental health professionals, friends, and family can make a significant difference. Remember, you are not alone, and help is available.
What Are the Clinical Features of a Suicidal Person?
Suicidal individuals often exhibit distinct warning signs that indicate emotional distress and a heightened risk of self-harm. These signs can be verbal, behavioral, or psychological, and recognizing them early can be life-saving. While each person’s experience with suicidal thoughts is different, there are common clinical features that may indicate someone is at risk.
1. Talking About Suicide
One of the most direct indicators of suicidal ideation is when a person expresses a desire to die. They may make statements such as:
- “I wish I were dead.”
- “I can’t do this anymore.”
- “I wish I hadn’t been born.”
- “Everyone would be better off without me.”
These verbal cues should always be taken seriously, as they reflect inner turmoil and a potential risk of self-harm.
2. Seeking the Means to End Their Life
A suicidal person may take active steps to plan their death. This could include researching methods of suicide, obtaining a weapon, stockpiling medications, or identifying a location where they intend to harm themselves. These actions indicate an urgent need for intervention.
3. Expressing Feelings of Hopelessness or Worthlessness
Many individuals struggling with suicidal thoughts feel as if their situation will never improve. They may believe they are a burden to others and that nothing they do will make a difference. Feelings of deep despair, extreme guilt, or self-hatred can intensify suicidal ideation.
4. Withdrawing from Social Interactions
People contemplating suicide often isolate themselves from friends, family, and social activities they once enjoyed. They may stop answering calls, avoid conversations, or refuse to leave their home. This detachment can signal a deep sense of loneliness and emotional exhaustion.
5. Engaging in Reckless or Self-Destructive Behavior
A suicidal person may exhibit dangerous behaviors, such as reckless driving, excessive drug or alcohol use, or engaging in activities with a high risk of injury. These behaviors suggest a lack of concern for personal safety and can be a cry for help.
Recognizing these clinical features is critical in providing timely intervention. If you or someone you know is displaying these signs, seeking professional support can provide the guidance and care needed to prevent a crisis. Remember, help is available, and no one has to face these struggles alone.
How Does Depression Affect Suicidal Thoughts?
Depression, especially when moderate or severe, can significantly increase the risk of suicidal thoughts. It often creates overwhelming feelings of hopelessness, worthlessness, and emotional pain, making it difficult to see a way forward. Individuals struggling with depression may experience persistent thoughts of self-harm or suicide, leading to increased risk if left untreated. If you or someone you love shows signs of withdrawal, despair, or drastic behavioral changes, it is crucial to seek professional help. Support from therapists, friends, and family can make a life-saving difference in overcoming suicidal thoughts and finding hope again. Help is always available.
How to Cope with Suicidal Thoughts in the Long Term
Seeking Professional Help
Professional therapy can provide the tools and guidance needed to address the root causes of suicidal thoughts. Uncover Counseling offers specialized therapy, including:
Effective Therapeutic Approaches
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps reframe negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) – Focuses on emotional regulation and distress tolerance.
- Psychodynamic Therapy – Explores past experiences to understand emotional struggles.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) – Encourages mindfulness and self-acceptance.
- Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT) – Challenges irrational beliefs that lead to distress.
- Prolonged Exposure Therapy – Helps process trauma-related distress.
Building a Strong Support System
- Surround yourself with positive, understanding people.
- Join support groups for those experiencing similar challenges.
Healthy Lifestyle Changes
- Prioritize sleep, exercise, and a balanced diet.
- Reduce alcohol and substance use.
- Engage in hobbies and activities that bring joy.
Finding Hope and Support
Knowing how to stop suicidal thoughts is an important step toward recovery. While these feelings can be overwhelming, support and resources are available to help you heal. If you or someone you know is struggling, professional therapy and crisis support can make a difference. Visit Uncover Counseling for expert guidance and compassionate care. You are not alone—help is always within reach. Book an appointment today!