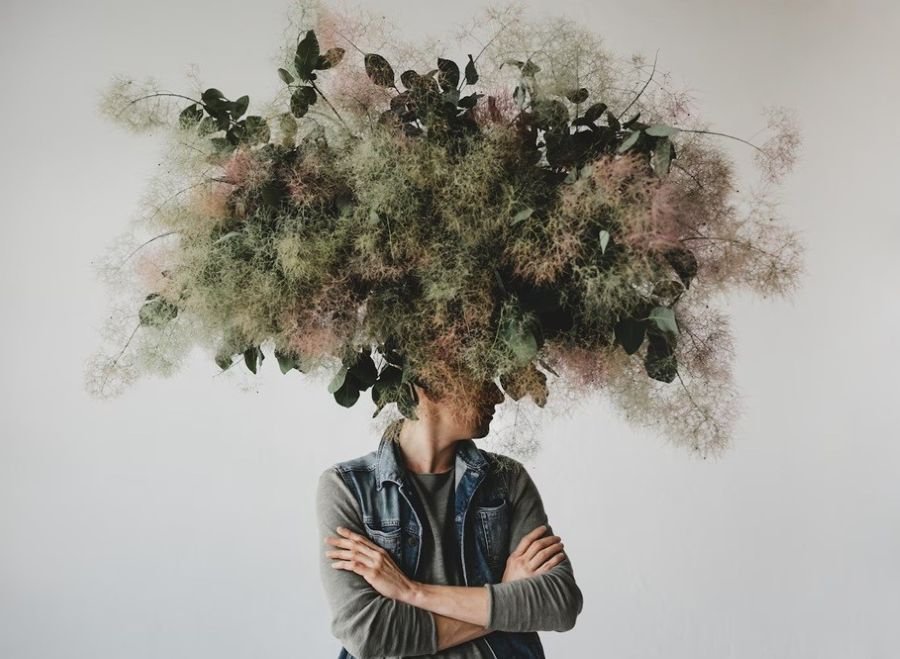
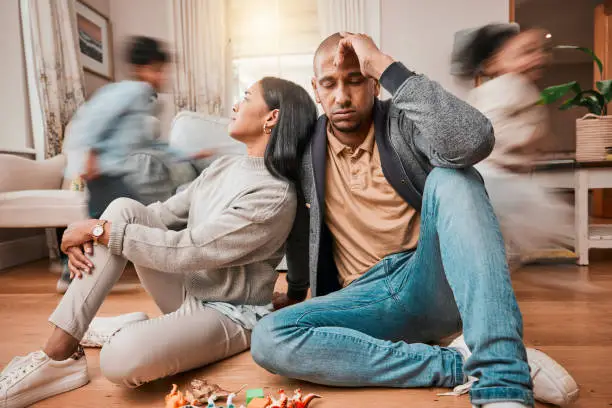
Everyone experiences emotions, but for some people, emotions can feel overwhelming, intense, and difficult to control. This phenomenon is known as emotional dysregulation—a condition where emotions are experienced in extremes and have a significant impact on daily life. Emotional dysregulation can affect relationships, work, and mental well-being, making it essential to understand and manage effectively.
What Is Emotional Dysregulation?

Emotional dysregulation refers to difficulty in managing emotional responses appropriately. It can result in intense mood swings, overwhelming feelings, and impulsive reactions. At the same time, everyone experiences emotional ups and downs, individuals with emotional dysregulation struggle to return to a calm state after experiencing distress.
This condition is often associated with mental health disorders such as borderline personality disorder (BPD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). However, emotional dysregulation can also stem from childhood experiences, trauma, or even prolonged stress.
Emotional Dysregulation Symptoms
People experiencing emotional dysregulation may exhibit various symptoms that affect daily functioning and relationships. These include:
- Intense Mood Swings: Rapid emotional shifts that can feel overwhelming and unpredictable.
- Difficulty Calming Down: Struggling to return to a baseline emotional state after distressing experiences.
- Impulsive Decision-Making: Acting on emotions without considering long-term consequences.
- Heightened Sensitivity: Reacting strongly to criticism, rejection, or perceived slights.
- Chronic Negative Emotions: Persistent feelings of frustration, anger, or sadness that seem difficult to control.
- Disproportionate Emotional Reactions: Experiencing outbursts that may seem excessive for the situation at hand.
These symptoms can significantly impact daily life, making it hard to maintain stable relationships, function effectively at work or school, and cultivate a sense of inner peace. Emotional dysregulation can lead to social withdrawal, difficulties in communication, and recurring conflicts with others. Over time, unmanaged symptoms may contribute to feelings of isolation, self-doubt, and decreased self-esteem. Recognizing these signs is an essential step toward seeking support and learning strategies to regain emotional balance.
Emotional Dysregulation in ADHD and BPD
Emotional dysregulation is commonly linked to ADHD and BPD, although it presents differently in each condition.
- ADHD: Individuals with ADHD often struggle with impulsivity and emotional intensity. They may react strongly to frustration, experience rejection sensitivity, and find it difficult to shift focus away from distressing emotions.
- BPD: Those with borderline personality disorder experience extreme emotional highs and lows. Their emotions may shift rapidly, leading to impulsive behaviors, unstable relationships, and chronic feelings of emptiness.
Understanding the link between emotional dysregulation and these conditions can help individuals find targeted treatment strategies.
The Link Between Emotional Dysregulation and ADHD
Emotional dysregulation ADHD is a well-documented concern. Individuals with ADHD often struggle with emotional control due to differences in brain structure and function. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for regulating emotions and impulse control, may not function as efficiently in those with ADHD, leading to difficulties in managing emotional responses.
If you or someone you love struggles with ADHD-related emotional dysregulation, seeking help from an ADHD Specialist NYC can provide valuable guidance and support in developing emotional management strategies.
How Emotional Dysregulation Affects Daily Life
Emotional dysregulation can impact various aspects of life, including:
Relationships
Frequent emotional outbursts and difficulty managing emotions can strain relationships with friends, family, and romantic partners. Relationship Therapy New York City can help individuals develop healthier ways to communicate and express emotions within relationships.
Work and Productivity
Unmanaged emotional dysregulation may lead to impulsive actions, frustration, and difficulty focusing, which can affect professional performance. Seeking Stress Management NYC services can help individuals develop coping strategies to enhance productivity and emotional balance.
Mental Health
Emotional dysregulation is often linked to conditions such as anxiety and depression. Therapist for Depression in NYC and Anxiety Therapist NYC services can provide essential therapeutic support to address these underlying issues.
Why Do Some People Feel Emotions More Intensely?
Some individuals experience emotions more intensely due to a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. People with heightened emotional sensitivity often have differences in brain function, particularly in areas responsible for emotion regulation, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
Additionally, childhood experiences play a significant role. Those who grew up in environments where emotions were dismissed, invalidated, or punished may have difficulty regulating their feelings. Emotional dysregulation can also develop from exposure to chronic stress or trauma, leading to an overactive stress response system.
The Role of Trauma and Childhood Experiences
Trauma, especially in early life, can disrupt emotional development and make regulation more challenging. Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), such as neglect, abuse, or exposure to violence, can shape the way individuals respond to emotions later in life.
Children who were not taught healthy coping mechanisms may develop maladaptive ways of handling distress, such as shutting down emotionally or reacting aggressively. Without intervention, these patterns can persist into adulthood, making emotional regulation difficult.
Why Do I Get Emotionally Dysregulated?
Emotional dysregulation often originates from early-life experiences that shape the brain’s response to stress and emotions. Stressful or life-altering events during childhood can lead to increased sensitivity in the central nervous system, making it more challenging to regulate emotions effectively even into adulthood.
Childhood trauma plays a significant role in emotional dysregulation. Experiences such as abuse, neglect, or exposure to domestic violence can create lasting effects on emotional processing. When caregivers fail to provide emotional validation or a safe environment, children may develop maladaptive coping mechanisms, such as emotional suppression, outbursts, or avoidance. These learned patterns can persist into adulthood, making it difficult to navigate stress and interpersonal relationships.
Additionally, growing up in an environment where emotions were dismissed or punished may contribute to dysregulation. Without guidance on how to process emotions constructively, individuals may struggle with overwhelming feelings or sudden mood swings.
Beyond childhood experiences, other factors such as chronic stress, trauma in adulthood, neurodivergent conditions like ADHD or BPD, and even genetics can contribute to emotional dysregulation. Recognizing the root causes of these emotional challenges is essential for developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support. Therapy, self-awareness, and mindfulness techniques can help rewire the brain’s response to stress and improve emotional regulation over time.
How to Stop Letting Emotions Control You?
Managing emotions effectively requires self-awareness and intentional practices that promote regulation. Here are some strategies to help regain control over your emotions:
- Take Deep Breaths: When emotions feel overwhelming, pause and focus on slow, deep breathing. This helps activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress and restoring a sense of calm. Inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth.
- Practice Meditation: Regular meditation, even for 10 to 20 minutes daily, enhances emotional awareness and resilience. Mindfulness meditation helps you observe emotions without immediate reaction, allowing for better decision-making and control.
- Acknowledge Your Feelings: Instead of suppressing or ignoring emotions, recognize and accept them. Labeling emotions can help decrease their intensity and allow for a more thoughtful response.
- Ask Better Questions: When emotions arise, take a moment to reflect on their root caus e. Ask yourself, “Why am I feeling this way?” and “What triggered this reaction?” Understanding the underlying reasons can provide clarity and help in developing healthier coping mechanisms.
- Engage in Grounding Techniques: Physical activities like walking, stretching, or using grounding exercises (such as the 5-4-3-2-1 technique) can help shift focus from emotional distress to the present moment.
By implementing these techniques consistently, you can build emotional resilience and prevent emotions from taking over your actions and decisions.
What Trauma Causes Emotional Dysregulation?
Emotional dysregulation is often linked to past experiences of interpersonal trauma, which can deeply affect emotional processing and stability. Unlike non-interpersonal trauma, which is more associated with PTSD and dissociative symptoms, interpersonal trauma plays a more direct role in emotional dysregulation.
- Childhood Abuse and Neglect: Experiencing physical, emotional, or sexual abuse in early life can disrupt the development of healthy emotional regulation. Neglect, where a child’s emotional needs are ignored, can also contribute to long-term difficulties in managing emotions.
- Multiple Interpersonal Traumas: Repeated exposure to abusive or traumatic relationships, including toxic family dynamics or abusive romantic partnerships, can heighten emotional instability. These experiences may lead to heightened sensitivity to rejection, difficulty trusting others, and intense emotional reactions.
- Domestic Violence and Betrayal Trauma: Growing up or living in an environment with domestic violence can make it difficult to regulate emotions, as the nervous system remains in a heightened state of alertness. Betrayal trauma, such as infidelity or abandonment by a trusted individual, can also contribute to dysregulation.
- Bullying and Social Rejection: Chronic bullying or exclusion in childhood or adulthood can create deep emotional wounds, making it harder to manage stress, regulate emotions, and maintain self-worth.
Recognizing the impact of trauma on emotional regulation is an important step toward healing. Therapy, self-awareness, and emotional regulation strategies can help individuals work through past trauma and regain control over their emotional responses.
Coping Strategies for Emotional Dysregulation
Managing emotional dysregulation is possible with the right tools and support. Here are some effective coping strategies:
1. Practice Mindfulness and Self-Awareness
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, help individuals become more aware of their emotional responses and develop a sense of calm in stressful situations.
2. Engage in Therapy
Different forms of therapy can provide significant benefits in managing emotional dysregulation. Some effective treatments include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to emotional distress.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): Focuses on developing emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Encourages acceptance of emotions while taking meaningful action towards a fulfilling life.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores past experiences to uncover patterns affecting emotional responses.
If you’re struggling with emotional regulation, reaching out to a Trauma Therapist NYC or seeking Anger Management Therapy in NYC can be a crucial step towards healing.
3. Identify and Challenge Negative Thoughts
Individuals with emotional dysregulation often experience distorted thinking patterns that amplify distress. Learning to identify and challenge these thoughts can help reframe emotions in a healthier way.
4. Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Replacing impulsive reactions with healthier coping mechanisms—such as journaling, engaging in physical activity, or talking to a trusted friend—can help regulate emotions more effectively.
5. Improve Self-Esteem
Low self-esteem can exacerbate emotional dysregulation. Seeking Self Esteem Therapy in NYC can assist in building confidence and resilience to better manage emotional challenges.
6. Using the STOP Technique
When emotions feel overwhelming, following the STOP technique can be beneficial:
- Stop: Pause before reacting.
- Take a deep breath.
- Observe your thoughts and feelings.
- Proceed with a mindful response.
7. Engaging in Physical Activity
Exercise helps regulate emotions by releasing endorphins, which promote feelings of well-being. Activities like walking, yoga, or dance can serve as effective outlets for emotional energy.
8. Developing Healthy Expression
Rather than suppressing emotions, finding healthy ways to express them is crucial. This might include talking to a trusted friend, writing in a journal, or engaging in creative activities like painting or music.
9. Practicing Emotional Validation
Validating emotions means acknowledging and accepting them without judgment. Instead of thinking, “I shouldn’t feel this way,” try, “It’s okay to feel this, and I will work through it.”
When to Seek Professional Help for Emotional Dysregulation
If emotional dysregulation significantly interferes with daily life, seeking professional help can be beneficial. Signs that professional support may be necessary include:
- Persistent difficulty controlling emotions
- Frequent impulsive behaviors that lead to negative consequences
- Severe mood swings that impact relationships
- Self-harming behaviors or suicidal thoughts
A licensed therapist can help individuals develop coping strategies, process past trauma, and build healthier emotional responses.
Seeking Professional Help

Emotional dysregulation can feel overwhelming, but professional support can make a significant difference. If you’re struggling with intense emotions, working with a qualified therapist at Uncover Counseling can provide valuable strategies tailored to your unique needs. Therapy options such as Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy and Prolonged Exposure Therapy can also be highly effective in helping individuals regain control over their emotions.
Building Emotional Resilience for Long-Term Stability
Emotional dysregulation can be challenging, but understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step toward managing it effectively. By recognizing the signs of emotional dysregulation, seeking appropriate therapy, and practicing coping strategies, individuals can learn to navigate their emotions more successfully. If you or a loved one is struggling with emotional dysregulation, consider reaching out to Uncover Counseling for professional guidance. With the right support, it is possible to build emotional resilience and lead a more balanced, fulfilling life. Book an appointment today!